Page 166 - Read Online
P. 166
Zhang et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.117 Page 3 of 9
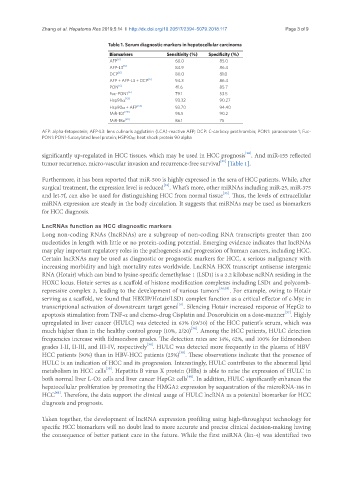
Table 1. Serum diagnostic markers in hepatocellular carcinoma
Biomarkers Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%)
AFP [6] 60.0 85.0
AFP-L3 [6] 84.9 86.4
DCP [6] 80.0 81.0
AFP + AFP-L3 + DCP [6] 94.3 86.4
PON [6] 41.6 85.7
Fuc-PON1 [6] 79.1 53.5
Hsp90α [53] 93.32 90.27
Hsp90α + AFP [53] 93.70 94.40
MiR-101 [28] 95.5 90.2
MiR-18a [29] 86.1 75
AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; AFP-L3: lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA)-reactive AFP; DCP: C-carboxy prothrombin; PON1: paraoxonase 1; Fuc-
PON1: PON1-fucosylated level protein; HSP90α: heat shock protein 90 alpha
[30]
significantly up-regulated in HCC tissues, which may be used in HCC prognosis . And miR-155 reflected
tumor recurrence, micro-vascular invasion and recurrence-free survival [Table 1].
[31]
Furthermore, it has been reported that miR-500 is highly expressed in the sera of HCC patients. While, after
[32]
surgical treatment, the expression level is reduced . What’s more, other miRNAs including miR-25, miR-375
and let-7f, can also be used for distinguishing HCC from normal tissue . Thus, the levels of extracellular
[33]
miRNA expression are steady in the body circulation. It suggests that miRNAs may be used as biomarkers
for HCC diagnosis.
LncRNAs function as HCC diagnostic markers
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a subgroup of non-coding RNA transcripts greater than 200
nucleotides in length with little or no protein-coding potential. Emerging evidence indicates that lncRNAs
may play important regulatory roles in the pathogenesis and progression of human cancers, including HCC.
Certain lncRNAs may be used as diagnostic or prognostic markers for HCC, a serious malignancy with
increasing morbidity and high mortality rates worldwide. LncRNA HOX transcript antisense intergenic
RNA (Hotair) which can bind to lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) is a 2.2 kilobase ncRNA residing in the
HOXC locus. Hotair serves as a scaffold of histone modification complexes including LSD1 and polycomb-
repressive complex 2, leading to the development of various tumors [34,35] . For example, owing to Hotair
serving as a scaffold, we found that HBXIP/Hotair/LSD1 complex function as a critical effector of c-Myc in
[36]
transcriptional activation of downstream target genes . Silencing Hotair increased response of HepG2 to
[37]
apoptosis stimulation from TNF-α and chemo-drug Cisplatin and Doxorubicin on a dose-manner . Highly
upregulated in liver cancer (HULC) was detected in 63% (19/30) of the HCC patient’s serum, which was
[38]
much higher than in the healthy control group (10%, 2/20) . Among the HCC patients, HULC detection
frequencies increase with Edmondson grades. The detection rates are 14%, 62%, and 100% for Edmondson
+
[38]
grades I-II, II-III, and III-IV, respectively . HULC was detected more frequently in the plasma of HBV
[38]
HCC patients (90%) than in HBV-HCC patients (25%) . These observations indicate that the presence of
HULC is an indication of HCC and its progression. Interestingly, HULC contributes to the abnormal lipid
metabolism in HCC cells . Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) is able to raise the expression of HULC in
[39]
[40]
both normal liver L-O2 cells and liver cancer HepG2 cells . In addition, HULC significantly enhances the
hepatocellular proliferation by promoting the HMGA2 expression by sequestration of the microRNA-186 in
[41]
HCC . Therefore, the data support the clinical usage of HULC lncRNA as a potential biomarker for HCC
diagnosis and prognosis.
Taken together, the development of lncRNA expression profiling using high-throughput technology for
specific HCC biomarkers will no doubt lead to more accurate and precise clinical decision-making having
the consequence of better patient care in the future. While the first miRNA (lin-4) was identified two