Page 111 - Read Online
P. 111
Chia et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:9 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.112 Page 3 of 14
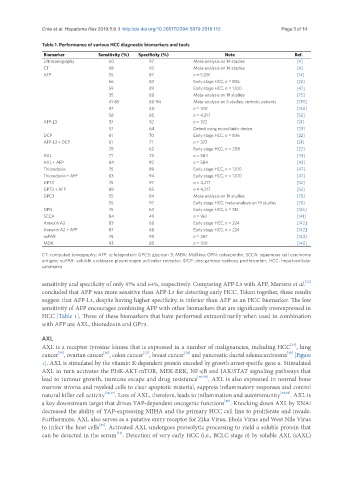
Table 1. Performance of various HCC diagnostic biomarkers and tools
Biomarker Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Note Ref.
Ultrasonography 60 97 Meta-analysis on 14 studies [4]
CT 68 93 Meta-analysis on 14 studies [4]
AFP 55 87 n = 5,581 [14]
66 82 Early stage HCC, n = 836 [22]
59 89 Early stage HCC, n = 1,100 [47]
35 88 Meta-analysis on 19 studies [75]
41-65 80-94 Meta-analysis on 5 studies, cirrhotic patients [139]
97 40 n = 100 [140]
58 85 n = 4,217 [52]
AFP-L3 37 92 n = 372 [21]
57 64 Detect using microfluidic device [23]
DCP 61 70 Early stage HCC, n = 836 [22]
AFP-L3 + DCP 61 71 n = 372 [21]
78 62 Early stage HCC, n = 208 [22]
AXL 71 73 n = 584 [43]
AXL + AFP 84 92 n = 584 [43]
Thioredoxin 75 89 Early stage HCC, n = 1,100 [47]
Thioredoxin + AFP 83 94 Early stage HCC, n = 1,100 [47]
GP73 75 97 n = 4,217 [52]
GP73 + AFP 89 85 n = 4,217 [52]
GPC3 55 84 Meta-analysis on 19 studies [75]
55 97 Early stage HCC, meta-analysis on 19 studies [75]
OPN 75 62 Early stage HCC, n = 312 [126]
SCCA 84 49 n = 961 [141]
Annexin A2 83 68 Early stage HCC, n = 224 [142]
Annexin A2 + AFP 87 68 Early stage HCC, n = 224 [142]
suPAR 76 90 n = 267 [143]
MDK 93 83 n = 100 [140]
CT: computed tomography; AFP: α-fetoprotein; GPC3: glypican 3; MDK: Midkine; OPN: osteopontin; SCCA: squamous cell carcinoma
antigen; suPAR: soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor; DCP: des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin; HCC: hepatocellular
carcinoma
[22]
sensitivity and specificity of only 57% and 64%, respectively. Comparing AFP-L3 with AFP, Marrero et al.
concluded that AFP was more sensitive than AFP-L3 for detecting early HCC. Taken together, these results
suggest that AFP-L3, despite having higher specificity, is inferior than AFP as an HCC biomarker. The low
sensitivity of AFP encourages combining AFP with other biomarkers that are significantly overexpressed in
HCC [Table 1]. Three of these biomarkers that have performed extraordinarily when used in combination
with AFP are AXL, thioredoxin and GP73.
AXL
[24]
AXL is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is expressed in a number of malignancies, including HCC , lung
[27]
[28]
[26]
[25]
[29]
cancer , ovarian cancer , colon cancer , breast cancer and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [Figure
1]. AXL is stimulated by the vitamin K-dependent protein encoded by growth-arrest-specific gene 6. Stimulated
AXL in turn activates the PI3K-AKT-mTOR, MEK-ERK, NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways that
lead to tumour growth, immune escape and drug resistance [30-35] . AXL is also expressed in normal bone
marrow stroma and myeloid cells to clear apoptotic material, suppress inflammatory responses and control
natural killer cell activity [36,37] . Loss of AXL, therefore, leads to inflammation and autoimmunity [38,39] . AXL is
[40]
a key downstream target that drives YAP-dependent oncogenic functions . Knocking down AXL by RNAi
decreased the ability of YAP-expressing MIHA and the primary HCC cell line to proliferate and invade.
Furthermore, AXL also serves as a putative entry receptor for Zika Virus, Ebola Virus and West Nile Virus
to infect the host cells . Activated AXL undergoes proteolytic processing to yield a soluble protein that
[41]
[42]
can be detected in the serum . Detection of very early HCC (i.e., BCLC stage 0) by soluble AXL (sAXL)