Page 427 - Read Online
P. 427
Page 4 of 8 Fu et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:39 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.29
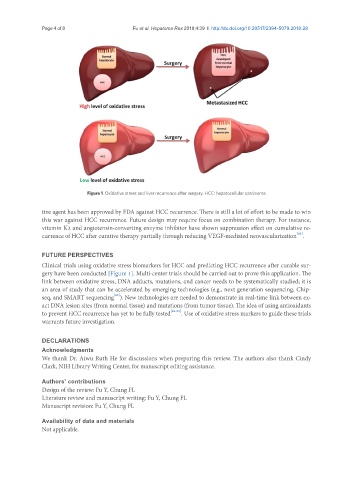
Figure 1. Oxidative stress and liver recurrence after surgery. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
tive agent has been approved by FDA against HCC recurrence. There is still a lot of effort to be made to win
this war against HCC recurrence. Future design may require focus on combination therapy. For instance,
vitamin K2 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor have shown suppression effect on cumulative re-
[81]
currence of HCC after curative therapy partially through reducing VEGF-mediated neovascularization .
FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
Clinical trials using oxidative stress biomarkers for HCC and predicting HCC recurrence after curable sur-
gery have been conducted [Figure 1]. Multi-center trials should be carried out to prove this application. The
link between oxidative stress, DNA adducts, mutations, and cancer needs to be systematically studied; it is
an area of study that can be accelerated by emerging technologies (e.g., next generation sequencing, Chip-
[82]
seq, and SMART sequencing ). New technologies are needed to demonstrate in real-time link between ex-
act DNA lesion sites (from normal tissue) and mutations (from tumor tissue). The idea of using antioxidants
to prevent HCC recurrence has yet to be fully tested [83-85] . Use of oxidative stress markers to guide these trials
warrants future investigation.
DECLARATIONS
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Aiwu Ruth He for discussions when preparing this review. The authors also thank Cindy
Clark, NIH Library Writing Center, for manuscript editing assistance.
Authors’ contributions
Design of the review: Fu Y, Chung FL
Literature review and manuscript writing: Fu Y, Chung FL
Manuscript revision: Fu Y, Chung FL
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.