Page 414 - Read Online
P. 414
Balsano et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:38 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.51 Page 3 of 12
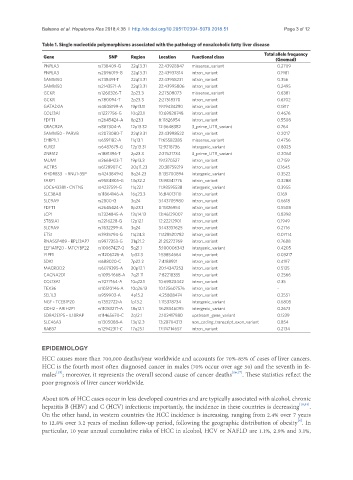
Table 1. Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with the pathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Total allele frequency
Gene SNP Region Location Functional class
(Gnomad)
PNPLA3 rs738409-G 22q13.31 22:43928847 missense_variant 0.2709
PNPLA3 rs2896019-G 22q13.31 22:43937814 intron_variant 0.1981
SAMM50 rs738491-T 22q13.31 22:43958231 intron_variant 0.356
SAMM50 rs2143571-A 22q13.31 22:43995806 intron_variant 0.2495
GCKR rs1260326-T 2p23.3 2:27508073 missense_variant 0.6381
GCKR rs780094-T 2p23.3 2:27518370 intron_variant 0.6702
GATAD2A rs4808199-A 19p13.11 19:19434290 intron_variant 0.1817
COL13A1 rs1227756-G 10q22.1 10:69828748 intron_variant 0.4676
FDFT1 rs2645424-A 8p23.1 8:11826954 intron_variant 0.5508
CRACR2A rs887304-A 12p13.32 12:3648382 3_prime_UTR_variant 0.764
SAMM50 - PARVB rs2073080-T 22q13.31 22:43998522 intron_variant 0.2017
EHBP1L1 rs6591182-A 11q13.1 11:65582285 missense_variant 0.4756
KLRG1 rs6487679-G 12p13.31 12:9218736 intergenic_variant 0.8025
ZNF512 rs1881396-T 2p23.3 2:27621734 3_prime_UTR_variant 0.2063
MUM1 rs2668423-T 19p13.3 19:1370527 intron_variant 0.7159
ACTR5 rs6128907-C 20q11.23 20:38759219 intron_variant 0.1645
KHDRBS3 - RNU1-35P rs4243849-G 8q24.23 8:135700894 intergenic_variant 0.3522
FARP1 rs9584805-G 13q32.2 13:98341776 intron_variant 0.3288
LOC643381 - CNTN5 rs4237591-G 11q22.1 11:98595538 intergenic_variant 0.3955
SLC38A8 rs11864146-A 16q23.3 16:84013110 intron_variant 0.169
SLC9A9 rs2800-G 3q24 3:143705980 intron_variant 0.6618
FDFT1 rs2645424-A 8p23.1 8:11826954 intron_variant 0.5508
LCP1 rs7324845-A 13q14.13 13:46129007 intron_variant 0.8398
ST8SIA1 rs2216228-G 12p12.1 12:22212901 intron_variant 0.1949
SLC9A9 rs7632299-A 3q24 3:143337625 intron_variant 0.2716
ETS1 rs3935794-G 11q24.3 11:128520782 intron_variant 0.07114
RNA5SP489 - RPL13AP7 rs9977253-G 21q21.2 21:25272769 intron_variant 0.7688
EEF1A1P20 - MTCYBP22 rs10067427-G 5q21.1 5:100006343 intergenic_variant 0.4205
YIPF1 rs11206226-A 1p32.3 1:53854664 intron_variant 0.03217
SDK1 rs688020-C 7p22.2 7:4188921 intron_variant 0.4197
MACROD2 rs6079395-A 20p12.1 20:14347253 intron_variant 0.5135
CACNA2D1 rs10954668-A 7q21.11 7:82218335 intron_variant 0.2566
COL13A1 rs7077164-A 10q22.1 10:69823442 intron_variant 0.35
TEX36 rs10510146-A 10q26.13 10:125607576 intron_variant -
SEL1L3 rs959903-A 4p15.2 4:25808474 intron_variant 0.2551
NGF - TCEB1P20 rs7552722-A 1p13.2 1:115378734 intergenic_variant 0.6805
CDH2 - ARIH2P1 rs11083271-A 18q12.1 18:28346095 intergenic_variant 0.2673
SDR42E1P5 - IL18RAP rs11465670-C 2q12.1 2:102417980 upstream_gene_variant 0.1239
SLC46A3 rs1305088-A 13q12.3 13:28704313 non_coding_transcript_exon_variant 0.854
RAB37 rs12942311-C 17q25.1 17:74714657 intron_variant 0.2134
EPIDEMIOLOGY
HCC causes more than 700,000 deaths/year worldwide and accounts for 70%-85% of cases of liver cancers.
HCC is the fourth most often diagnosed cancer in males (70% occur over age 50) and the seventh in fe-
[15]
males ; moreover, it represents the overall second cause of cancer deaths [16,17] . These statistics reflect the
poor prognosis of liver cancer worldwide.
About 80% of HCC cases occur in less developed countries and are typically associated with alcohol, chronic
hepatitis B (HBV) and C (HCV) infections: importantly, the incidence in these countries is decreasing [18,19] .
On the other hand, in western countries the HCC incidence is increasing, ranging from 2.4% over 7 years
[4]
to 12.8% over 3.2 years of median follow-up period, following the geographic distribution of obesity . In
particular, 10 year annual cumulative risks of HCC in alcohol, HCV or NAFLD are 1.1%, 2.9% and 3.1%,