Page 290 - Read Online
P. 290
Lin et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:26 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.27 Page 5 of 8
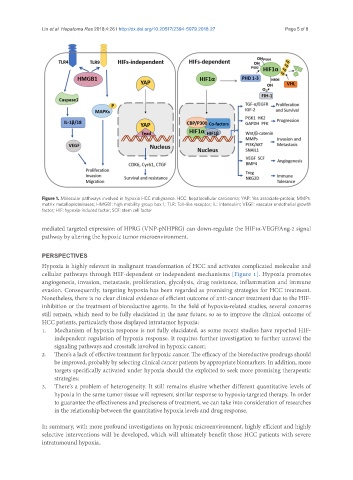
Figure 1. Molecular pathways involved in hypoxia HCC malignance. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; YAP: Yes associate-protein; MMPs:
matrix metalloproteinases; HMGB1: high mobility group box 1; TLR: Toll-like receptor; IL: interleukin; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth
factor; HIF: hypoxia-induced factor; SCF: stem cell factor
mediated targeted expression of HPRG (VNP-pNHPRG) can down-regulate the HIF1α-VEGF/Ang-2 signal
pathway by altering the hypoxic tumor microenvironment.
PERSPECTIVES
Hypoxia is highly relevant in malignant transformation of HCC and activates complicated molecular and
cellular pathways through HIF-dependent or independent mechanisms [Figure 1]. Hypoxia promotes
angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, proliferation, glycolysis, drug resistance, inflammation and immune
evasion. Consequently, targeting hypoxia has been regarded as promising strategies for HCC treatment.
Nonetheless, there is no clear clinical evidence of efficient outcome of anti-cancer treatment due to the HIF-
inhibition or the treatment of bioreductive agents. In the field of hypoxia-related studies, several concerns
still remain, which need to be fully elucidated in the near future, so as to improve the clinical outcome of
HCC patients, particularly those displayed intratumor hypoxia:
1. Mechanism of hypoxia response is not fully elucidated, as some recent studies have reported HIF-
independent regulation of hypoxia response. It requires further investigation to further unravel the
signaling pathways and crosstalk involved in hypoxic cancer;
2. There’s a lack of effective treatment for hypoxic cancer. The efficacy of the bioreductive prodrugs should
be improved, probably by selecting clinical cancer patients by appropriate biomarkers. In addition, more
targets specifically activated under hypoxia should the exploited to seek more promising therapeutic
strategies;
3. There’s a problem of heterogeneity. It still remains elusive whether different quantitative levels of
hypoxia in the same tumor tissue will represent similar response to hypoxia-targeted therapy. In order
to guarantee the effectiveness and preciseness of treatment, we can take into consideration of researches
in the relationship between the quantitative hypoxia levels and drug response.
In summary, with more profound investigations on hypoxic microenvironment, highly efficient and highly
selective interventions will be developed, which will ultimately benefit those HCC patients with severe
intratumoural hypoxia..