Page 251 - Read Online
P. 251
Page 4 of 14 Irshad et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.25
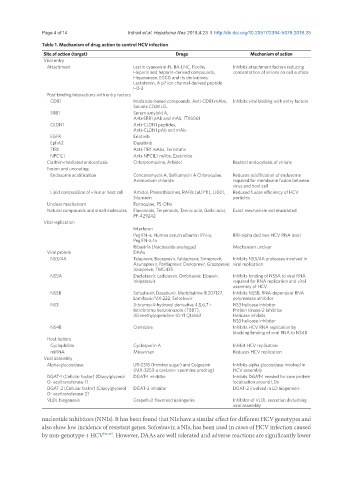
Table 1. Mechanism of drug action to control HCV infection
Site of action (target) Drugs Mechanism of action
Viral entry
Attachment Lectin cyanovirin-N, BA-LNC, Ficolin, Inhibits attachment factors reducing
Heparin and heparin-derived compounds, concentration of virions on cell surface
Heparanase, EGCG and its derivatives,
Lactoferrin, A p7 ion channel-derived peptide
H2-3
Post-binding interactions with entry factors
CD81 Imidazole-based compounds, Anti-CD81 mAbs, Inhibits viral binding with entry factors
Soluble CD81 LEL
SRB1 Serum amyloid A,
Anti-SRB1 pAb and mAb, ITX5061
CLDN1 Anti-CLDN1 peptides,
Anti-CLDN1 pAb and mAb
EGFR Erlotinib
EphA2 Dasatinib
TfR1 Anti-TfR1 mAbs, Ferristatin
NPC1L1 Anti-NPC1L1 mAbs, Ezetimibe
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis Chlorpromazine, Arbidol Restrict endocytosis of virions
Fusion and uncoating
Endosome acidification Concanamycin A, Bafilomycin A Chloroquine, Reduces acidification of endosome
Ammonium chloride required for membrane fusion between
virus and host cell
Lipid composition of virus or host cell Arbidol, Phenothiazines, RAFIs (aUY11), LJ001, Reduced fusion efficiency of HCV
Silymarin particles
Unclear mechanism Ferroquine, PS-ONs
Natural compounds and small molecules Flavonoids, Terpenoids, Tannic acid, Gallic acid, Exact mechanism not elucidated
PF-429242
Viral replication
Interferon
PegIFN-α, Human serum albumin IFN-α, IFN-alpha declines HCV RNA level
PegIFN-λ-1a
Ribavirin (Nucleoside analogue) Mechanism unclear
Viral protein DAAs
NS3/4A Telaprevir, Boceprevir, Faldaprevir, Simeprevir, Inhibits NS3/4A proteases involved in
Asunaprevir, Paritaprevir, Danoprevir, Grazoprevir, viral replication
Vaniprevir, TMC435
NS5A Daclatasvir, Ledipasvir, Ombitasvir, Elbasvir, Inhibits binding of NS5A to viral RNA
Velpatasvir required for RNA replication and viral
assembly of HCV
NS5B Sofosbuvir, Dasabuvir, Mericitabine BI207127, Inhibits NS5B, RNA-dependent RNA
Lomibuvir/VX-222, Setrobuvir polymerase inhibitor
NS3 3-bromo-4-hydroxyl derivative 4,5,6,7 – NS3 helicase inhibitor
tetrobromo benzotriazole (TBBT), Protein kinase-2 inhibitor
30-methylpiperidine-10-Yl QU663 Helicase inhibits
NS3 helicase inhibitor
NS4B Clemizole Inhibits HCV RNA replication by
blocking binding of viral RNA to NS4B
Host factors
Cyclophilins Cyclosporin A Inhibit HCV replication
miRNA Miravirsen Reduces HCV replication
Viral assembly
Alpha-glucosidase UT-231B (Immino sugar) and Celgosivir Inhibits alpha glucosidase involved in
(MX-3253-a castano- spermine prodrug) HCV assembly
DGAT-1 (Cellular factor) (Diacylglycerol DGAT-1 inhibitor Inhibits DGAT-1 needed for core protein
O- acyltransferase-1) localization around LDs
DGAT-2 (Cellular factor) (Diacylglycerol DGAT-2 inhibitor DGAT-2 involved in LD biogenesis
O- acyltransferase-2)
VLDL biogenesis Grapefruit flavonoid naringenin Inhibitor of VLDL secretion disturbing
viral assembly
nucleotide inhibitors (NNIs). It has been found that NIs have a similar effect for different HCV genotypes and
also show low incidence of resistant genes. Sofosbuvir, a NIs, has been used in cases of HCV infection caused
by non-genotype-1 HCV [31,32] . However, DAAs are well tolerated and adverse reactions are significantly lower