Page 226 - Read Online
P. 226
Page 4 of 10 Lu et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:21 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.44
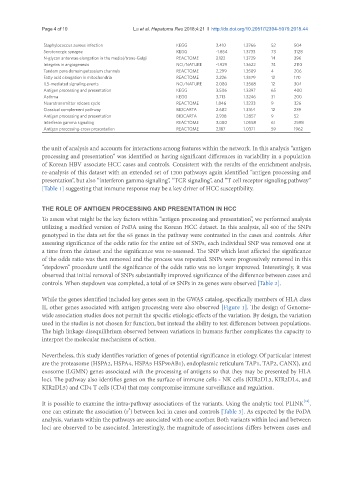
Staphylococcus aureus infection KEGG 3.410 1.3766 52 504
Serotonergic synapse KEGG -1.854 1.3733 73 3128
N-glycan antennae elongation in the medial/trans-Golgi REACTOME 2.122 1.3729 14 396
Integrins in angiogenesis NCI/NATURE -1.929 1.3622 74 2110
Tandem pore domain potassium channels REACTOME 2.299 1.3589 4 206
Fatty acid elongation in mitochondria REACTOME 2.226 1.3579 12 170
IL5-mediated signaling events NCI/NATURE 2.080 1.3568 12 304
Antigen processing and presentation KEGG 3.506 1.3397 65 400
Asthma KEGG 3.713 1.3246 31 200
Neurotransmitter release cycle REACTOME 1.846 1.3233 9 326
Classical complement pathway BIOCARTA 2.682 1.3164 12 239
Antigen processing and presentation BIOCARTA 2.938 1.2857 9 52
Interferon gamma signaling REACTOME 3.080 1.0558 61 2598
Antigen processing-cross presentation REACTOME 2.187 1.0371 59 1962
the unit of analysis and accounts for interactions among features within the network. In this analysis “antigen
processing and presentation” was identified as having significant differences in variability in a population
of Korean HBV associate HCC cases and controls. Consistent with the results of the enrichment analysis,
re-analysis of this dataset with an extended set of 1200 pathways again identified “antigen processing and
presentation”, but also “interferon gamma signaling”, “TCR signaling”, and “T cell receptor signaling pathway”
[Table 1] suggesting that immune response may be a key driver of HCC susceptibility.
THE ROLE OF ANTIGEN PROCESSING AND PRESENTATION IN HCC
To assess what might be the key factors within “antigen processing and presentation”, we performed analysis
utilizing a modified version of PoDA using the Korean HCC dataset. In this analysis, all 400 of the SNPs
genotyped in the data set for the 65 genes in the pathway were contrasted in the cases and controls. After
assessing significance of the odds ratio for the entire set of SNPs, each individual SNP was removed one at
a time from the dataset and the significance was re-assessed. The SNP which least affected the significance
of the odds ratio was then removed and the process was repeated. SNPs were progressively removed in this
“stepdown” procedure until the significance of the odds ratio was no longer improved. Interestingly, it was
observed that initial removal of SNPs substantially improved significance of the difference between cases and
controls. When stepdown was completed, a total of 49 SNPs in 26 genes were observed [Table 2].
While the genes identified included key genes seen in the GWAS catalog, specifically members of HLA class
II, other genes associated with antigen processing were also observed [Figure 1]. The design of Genome-
wide association studies does not permit the specific etiologic effects of the variation. By design, the variation
used in the studies is not chosen for function, but instead the ability to test differences between populations.
The high linkage disequilibrium observed between variations in humans further complicates the capacity to
interpret the molecular mechanisms of action.
Nevertheless, this study identifies variation of genes of potential significance in etiology. Of particular interest
are the proteasome (HSPA2, HSPA4, HSPA5 HSP90AB1), endoplasmic reticulum TAP1, TAP2, CANX), and
exosome (LGMN) genes associated with the processing of antigens so that they may be presented by HLA
loci. The pathway also identifies genes on the surface of immune cells - NK cells (KIR2DL3, KIR2DL4, and
KIR2DL5) and CD4 T cells (CD4) that may compromise immune surveillance and regulation.
[18]
It is possible to examine the intra-pathway associations of the variants. Using the analytic tool PLINK ,
2
one can estimate the association (r ) between loci in cases and controls [Table 3]. As expected by the PoDA
analysis, variants within the pathways are associated with one another. Both variants within loci and between
loci are observed to be associated. Interestingly, the magnitude of associations differs between cases and