Page 67 - Read Online
P. 67
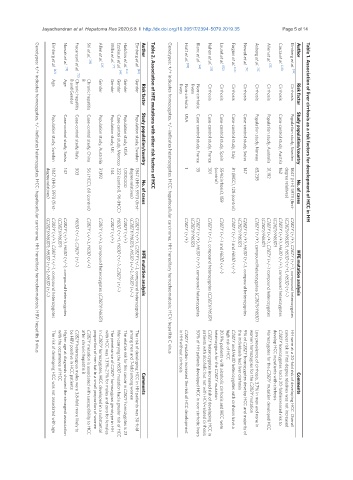
Jayachandran et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.35 Page 5 of 14 Table 1. Association of liver cirrhosis as a risk factors for development of HCC in HH
Author
Author
Shi et al. [56]
Allen et al. [23]
Willis et al. [71]
Allen et al. [23]
Hiatt et al. [69]
Lauret et al. [52]
Cauza et al. [48]
Nahon et al. [53]
Blanc et al. [68]
Nowak et al. [73]
Nowak et al. [73]
Asberg et al. [62]
Fargion et al. [40]
Elmberg et al. [42]
Elmberg et al. [42]
Haddow et al. [44]
Ezzikouri et al. [49]
Elmberg et al. [42]
Fracanzani et al. [72]
B
Age
Age
Gender
Gender
Gender
Gender
Gender
livers
livers
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
B and Gender
Risk factor
Risk factor
Non-cirrhotic
Non-cirrhotic
Chronic hepatitis
Chronic hepatitis
USA
Population study, UK
Population study, USA
Case-control study, Italy
Case-control study, Italy
Population study, Sweden
Case-control study, Swiss
Case-control study, Spain
Population study, Norway
Population study, Sweden
Case-control study, Swiss
Population study, Sweden
Case-control study, China
Case-control study, France
Case-control study, France
Population study, Australia
Population study, Australia
Study population/country
Case-control study, Austria
Study population/country
Case-control study, Morocco
1
35
301
162
147
147
303
144
31,192
31,192
65,238
(control)
1,000,000
Table 2. Association of HFE mutations with other risk factors of HCC
degree relatives)
degree relatives)
degree relatives)
554(cirrhosis), 159
No. of cases
No. of cases
1847 (HH) 5973 (first-
1847 (HH), 5973 (first-
56 (HCC), 60 (control)
1847 (HH), 5973 (first-
81 (HCC), 128 (control)
222 (control), 96 (HCC)
C282Y (+/+)
C282Y (+/+)
C282Y (+/+)
(C282Y/H63D)
(C282Y/H63D)
(C282Y/H63D)
(C282Y/H63D)
(C282Y/H63D)
H63D (+/−), C282Y (+/−)
C282Y (+/+), H63D (+/+)
C282Y (+/−) and H63D (+/−)
C282Y (+/−) and H63D (+/−)
H63D (+/+), H63D (+/−), C282Y (+/−)
HFE mutation analysis
HFE mutation analysis
(C282Y/H63D), H63D (+/+), H63D (+/−)
(C282Y/H63D), H63D (+/+), H63D (+/−)
(C282Y/H63D), H63D (+/+), H63D (+/−)
C282Y (+/+), H63D (+/−), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), H63D (+/−), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), H63D (+/+), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), C282Y (+/−) compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), H63D (+/+), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), C282Y (+/−), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), C282Y (+/−), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/+), C282Y (+/−), compound heterozygotes
C282Y (+/−), compound heterozygotes (C282Y/H63D)
C282Y (+/+), compound heterozygotes (C282Y/H63D)
C282Y (+/+), compound heterozygotes (C282Y/H63D)
Genotypes: +/+ indicates homozygotes, +/− indicates heterozygotes. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; HH: hereditary hemochromatosis; HBV: hepatitis B virus
Genotypes: +/+ indicates homozygotes, +/− indicates heterozygotes. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; HH: hereditary hemochromatosis; HCV: hepatitis C virus
high risk of HCC
in HH without cirrhosis
after chronic hepatitis B
with the occurrence of HCC
be HBV positive in HCC patients
the individuals had liver cirrhosis
Comments
Comments
heterozygous for the C282Y mutation
develop HCC in patients with cirrhosis
among men and 7-fold among women
women homozygous for the C282Y mutation
C282Y homozygotes had a 20-fold increased risk to
cancer risk in first-degree relatives was not increased
Low prevalence of cirrhosis, 3.7% in men and none in
HH were at a 20-fold risk of developing HCC. Overall
proportion of men but in a small proportion of women
C282Y and H63D heterozygotes with cirrhosis have a
20.9% patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and HCC were
Homozygotes for the C282Y mutation developed HCC
The risk of developing HCC in HH patients was 30-fold
The risk of developing HCC was not associated with age
The penetrance of C282Y homozygous genotype in HH
C282Y heterozygous males were 3.8-fold more likely to
with HCC was 1.31%-2.1% for males and zero for females
In C282Y homozygotes, HCC developed in a substantial
C282Y mutation increased the risk of HCC development
The relative risk for this cancer in C282Y homozygotes is 23
C282Y mutation is associated with susceptibility to HCC
9% of C282Y homozygotes develop HCC and majority of
patients with alcoholic but not with HCV-related cirrhosis
50% of HH patients developed HCC in non-cirrhotic livers
Higher age at diagnosis showed the strongest association
Men carrying the H63D mutation had a greater risk of HCC
C282Y heterozygotes increased risk of developing HCC in