Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Page 4 of 17 Shrestha et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.24
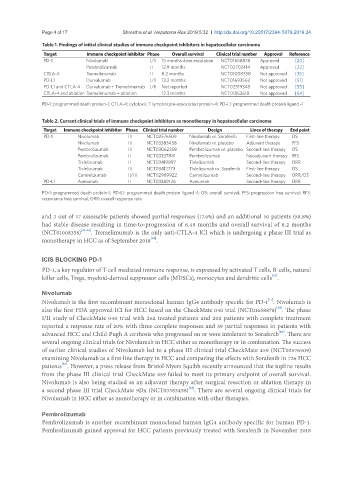
Table 1. Findings of initial clinical studies of immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma
Target Immune checkpoint inhibitor Phase Overall survival Clinical trial number Approval Reference
PD-1 Nivolumab I/II 15 months dose escalation NCT01658878 Approved [20]
Pembrolizumab II 12.9 months NCT02702414 Approved [22]
CTLA-4 Tremelimumab II 8.2 months NCT01008358 Not approved [35]
PD-L1 Durvalumab I/II 13.2 months NCT01693562 Not approved [51]
PD-L1 and CTLA-4 Durvalumab + Tremelimumab I/II Not reported NCT02519348 Not approved [55]
CTLA-4 and ablation Tremelimumab + ablation 12.3 months NCT01853618 Not approved [64]
PD-1: programmed death protein-1; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein-4; PD-L1: programmed death protein ligand -1
Table 2. Current clinical trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors as monotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma
Target Immune checkpoint inhibitor Phase Clinical trial number Design Lines of therapy End point
PD-1 Nivolumab III NCT02576509 Nivolumab vs. Sorafenib First-line therapy OS
Nivolumab III NCT03383458 Nivolumab vs. placebo Adjuvant therapy PFS
Pembrolizumab III NCT03062358 Pembrolizumab vs. placebo Second-line therapy OS
Pembrolizumab II NCT03337841 Pembrolizumab Neoadjuvant therapy RFS
Tislelizumab II NCT03419897 Tislelizumab Second-line therapy ORR
Tislelizumab III NCT03412773 Tislelizumab vs. Sorafenib First-line therapy OS
Camrelizumab II/III NCT02989922 Camrelizumab Second-line therapy ORR/OS
PD-L1 Avelumab II NCT03389126 Avelumab Second-line therapy ORR
PD-1: programmed death protein-1; PD-L1: programmed death protein ligand -1; OS: overall survival; PFS: progression free survival; RFS:
recurrence free survival; ORR: overall response rate
and 3 out of 17 assessable patients showed partial responses (17.6%) and an additional 10 patients (58.8%)
had stable disease resulting in time-to-progression of 6.48 months and overall survival of 8.2 months
(NCT01008358) [35,36] . Tremelimumab is the only anti-CTLA-4 ICI which is undergoing a phase III trial as
monotherapy in HCC as of September 2018 .
[28]
ICIS BLOCKING PD-1
PD-1, a key regulator of T-cell mediated immune response, is expressed by activated T cells, B-cells, natural
killer cells, Tregs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), monocytes and dendritic cells .
[37]
Nivolumab
[11]
Nivolumab is the first recombinant monoclonal human IgG4 antibody specific for PD-1 . Nivolumab is
also the first FDA approved ICI for HCC based on the CheckMate 040 trial (NCT01658878) . The phase
[20]
I/II study of CheckMate 040 trial with 262 treated patients and 202 patients with complete treatment
reported a response rate of 20% with three complete responses and 39 partial responses in patients with
[20]
advanced HCC and Child-Pugh A cirrhosis who progressed on or were intolerant to Sorafenib . There are
several ongoing clinical trials for Nivolumab in HCC either as monotherapy or in combination. The success
of earlier clinical studies of Nivolumab led to a phase III clinical trial CheckMate 459 (NCT02576509)
examining Nivolumab as a first-line therapy in HCC and comparing the effects with Sorafenib in 726 HCC
[38]
patients . However, a press release from Bristol-Myers Squibb recently announced that the topline results
from the phase III clinical trial CheckMate 459 failed to meet its primary endpoint of overall survival.
Nivolumab is also being studied as an adjuvant therapy after surgical resection or ablation therapy in
[28]
a second phase III trial CheckMate 9Dx (NCT03383458) . There are several ongoing clinical trials for
Nivolumab in HCC either as monotherapy or in combination with other therapies.
Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab is another recombinant monoclonal human IgG4 antibody specific for human PD-1.
Pembrolizumab gained approval for HCC patients previously treated with Sorafenib in November 2018