Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
Ni et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:25 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.14 Page 9 of 12
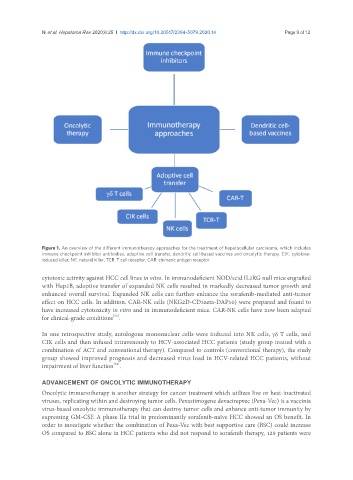
Figure 1. An overview of the different immunotherapy approaches for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, which includes
immune checkpoint inhibitor antibodies, adoptive cell transfer, dendritic cell-based vaccines and oncolytic therapy. CIK: cytokine-
induced killer; NK: natural killer; TCR: T cell receptor; CAR: chimeric antigen receptor
cytotoxic activity against HCC cell lines in vitro. In immunodeficient NOD/scid IL2RG null mice engrafted
with Hep3B, adoptive transfer of expanded NK cells resulted in markedly decreased tumor growth and
enhanced overall survival. Expanded NK cells can further enhance the sorafenib-mediated anti-tumor
effect on HCC cells. In addition, CAR-NK cells (NKG2D-CD3zeta-DAP10) were prepared and found to
have increased cytotoxicity in vitro and in immunodeficient mice. CAR-NK cells have now been adapted
[52]
for clinical-grade conditions .
In one retrospective study, autologous mononuclear cells were induced into NK cells, gd T cells, and
CIK cells and then infused intravenously to HCV-associated HCC patients (study group treated with a
combination of ACT and conventional therapy). Compared to controls (conventional therapy), the study
group showed improved prognosis and decreased virus load in HCV-related HCC patients, without
[53]
impairment of liver function .
ADVANCEMENT OF ONCOLYTIC IMMUNOTHERAPY
Oncolytic immunotherapy is another strategy for cancer treatment which utilizes live or heat-inactivated
viruses, replicating within and destroying tumor cells. Pexastimogene devacirepvec (Pexa-Vec) is a vaccinia
virus-based oncolytic immunotherapy that can destroy tumor cells and enhance anti-tumor immunity by
expressing GM-CSF. A phase IIa trial in predominantly sorafenib-naïve HCC showed an OS benefit. In
order to investigate whether the combination of Pexa-Vec with best supportive care (BSC) could increase
OS compared to BSC alone in HCC patients who did not respond to sorafenib therapy, 129 patients were