Page 31 - Read Online
P. 31
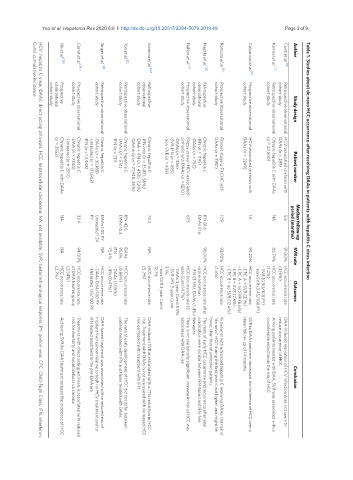
Yoo et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:9 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.49 Page 3 of 9 Table 1. Studies about de novo HCC occurrence after receiving DAAs in patients with hepatitis C virus infection
Author
Ide et al. [25]
Yoo et al. [22]
Conti et al. [14]
Singer et al. [23]
Carrat et al. [24]
Nahon et al. [21]
Kanwal et al. [17]
Nagata et al. [20]
Romano et al. [19]
Ioannou et al. [42]
Calvaruso et al. [18]
CumI: cumulative incidence
Prospective
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
cohort study
observational
observational
observational
Retrospective
Retrospective
Study design
Prospective observational
Prospective observational
Prospective observational
Prospective observational
Retrospective observational
Retrospective observational
Retrospective observational
Retrospective observational
(n = 2552)
(n = 22,500)
-IFN (n = 211)
-IFN (n = 1145)
DAAs (n = 285)
-DAAs (n = 752)
DAAs (n = 3917)
-IFN (n =1 2,948)
-DAAs (n = 574)
DAAs (n = 2249)
-DAAs (n = 336)
-DAA (n = 7344)
Chronic hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C
-non-SVR (n = 439)
-SVR-IFN (n = 495)
-DAAs (n = 30,183)
-Untreated (n = 2551)
Patient number
-Untreated (n = 137,502)
-IFN only (n = 35,871, 58%)
-DAA only (n = 21,948, 35%)
Fibrosis stage ≥ F3 CHC with
-DAA + IFN (n = 4535, 7.2%)
HCV-associated cirrhosis with
HCV-associated cirrhosis with
Chronic hepatitis C with DAAs
Chronic hepatitis C with DAAs
cirrhosis with DAAs (n = 1270)
Biopsy-proven HCV-associated
14
PY
NA
5.6
NA
17.9
33.4
73.2
67.5
IFN 81.6
IFN 43.6
DAAs 21.6
DAAs 10.4
period (months)
Median follow-up
DAAs 1.05 PY
Untreated 1.24
NA
NA
NA
IFN
75.4%
95.1%
DAAs
86.74%
93.90%
91.00%
96.00%
95.20%
94.00%
SVR rate
3.1%
12.7%
(1.4%)
(5.2%)
(2.7%)
(1.2%)
(3.16%)
(2.54%)
(0.89%)
- IFN (0.47%)
viral eradication
- DAAs (1.05%)
year-CumI 14.7%)
Outcomes
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
HCC occurrence rate
- DAAs 0.64/100 PY
- SVR (0.90/100 PY)
of DAA treated group
- CPC B + SVR (7.8%)
- CPC A + SVR (2.1%)
- SVR-IFN 3-year CumI:
- Untreated 1.18/100 PY
- non-SVR 3-year CumI:
HCC occurrence rate (5
- non-SVR (3.45/100 PY)
- CPC A + no SVR (6.6%)
- CPC B + no SVR (12.4%)
- IFN (3.3%), DAAs (1.4%)
HCC occurrence rate after
- DAAs 3-year CumI: 5.9%
therapies
associated with DAA use
reduce occurrence of HCC
mean follow-up of 14 months
lower, than that of untreated patients
risk compared with treatment with IFN
Conclusion
IFN-based treatment in the pre-DAA era
considerable reduction in the risk of HCC
risk for mortality and hepatocellular carcinoma
patients treated with IFN and those treated with DAAs
eradication were similar between IFN-based and IFN-free
DAA-induced resolution of HCV infection does not seem to
The risks of early HCC occurrence and recurrence after viral
DAA-based treatment was associated with a reduced risk of
The rate of early development of HCC did not differ between
DAA-induced SVR is associated with a 71% reduction in HCC
There is no statistically significant increase in risk of HCC was
incident liver cancer relative to both no HCV treatment and to
“de novo” HCC during the first year is not higher, and might be
Among patients treated with DAA, SVR was associated with a
SVR to DAA treatment decreased the incidence of HCC over a
Achieving SVR by DAA treatment reduces the incidence of HCC
In patients with advanced hepatitis C receiving DAAs, the risk of
risk. Treatment with DAAs is not associated with increased HCC
Treatment with direct-acting antivirals is associated with reduced
HCV: hepatitis C virus; DAAs: direct-acting antivirals; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; NA: not available; SVR: sustained virological response; PY: person-year; CPC: Child-Pugh Class; IFN: interferon;