Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Page 4 of 12 Jayachandran et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:44 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.59
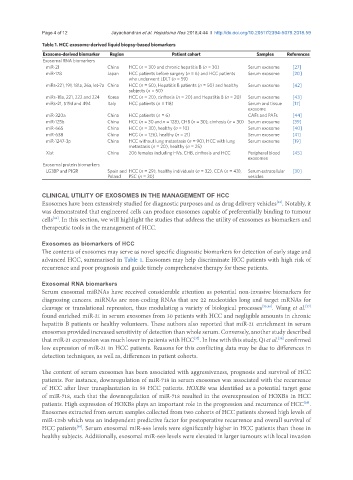
Table 1. HCC exosome-derived liquid biopsy-based biomarkers
Exosome-derived biomarker Region Patient cohort Samples References
Exosomal RNA biomarkers
miR-21 China HCC (n = 30) and chronic hepatitis B (n = 30) Serum exosome [27]
miR-178 Japan HCC patients before surgery (n = 6) and HCC patients Serum exosome [20]
who underwent LDLT (n = 59)
miRs-221, 191, 181a, 26a, let-7a China HCC (n = 50), Hepatitis B patients (n = 50) and healthy Serum exosome [42]
subjects (n = 50)
miRs-18a, 221, 222 and 224 Korea HCC (n = 20), cirrhosis (n = 20) and Hepatitis B (n = 20) Serum exosome [43]
miRs-21, 519d and 494 Italy HCC patients (n = 118) Serum and tissue [17]
exosome
miR-320a China HCC patients (n = 6) CAFs and PAFs [44]
miR-125b China HCC (n = 30 and n = 128), CHB (n = 30), cirrhosis (n = 30) Serum exosome [39]
miR-665 China HCC (n = 30), healthy (n = 10) Serum exosome [40]
miR-638 China HCC (n = 126), healthy (n = 21) Serum exosome [41]
miR-1247-3p China HCC without lung metastasis (n = 90), HCC with lung Serum exosome [19]
metastasis (n = 20), healthy (n = 25)
Xist China 206 females including HVs, CHB, cirrhosis and HCC Peripheral blood [45]
exosomes
Exosomal protein biomarkers
LG3BP and PIGR Spain and HCC (n = 29), healthy individuals (n = 32), CCA (n = 43), Serum extracellular [30]
Poland PSC (n = 30) vesicles
CLINICAL UTILITY OF EXOSOMES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HCC
Exosomes have been extensively studied for diagnostic purposes and as drug delivery vehicles . Notably, it
[33]
was demonstrated that engineered cells can produce exosomes capable of preferentially binding to tumour
cells . In this section, we will highlight the studies that address the utility of exosomes as biomarkers and
[34]
therapeutic tools in the management of HCC.
Exosomes as biomarkers of HCC
The contents of exosomes may serve as novel specific diagnostic biomarkers for detection of early stage and
advanced HCC, summarised in Table 1. Exosomes may help discriminate HCC patients with high risk of
recurrence and poor prognosis and guide timely comprehensive therapy for these patients.
Exosomal RNA biomarkers
Serum exosomal miRNAs have received considerable attention as potential non-invasive biomarkers for
diagnosing cancers. miRNAs are non-coding RNAs that are 22 nucleotides long and target mRNAs for
cleavage or translational repression, thus modulating a variety of biological processes [35,36] . Wang et al.
[27]
found enriched miR-21 in serum exosomes from 30 patients with HCC and negligible amounts in chronic
hepatitis B patients or healthy volunteers. These authors also reported that miR-21 enrichment in serum
exosomes provided increased sensitivity of detection than whole serum. Conversely, another study described
that miR-21 expression was much lower in patients with HCC . In line with this study, Qi et al. confirmed
[38]
[37]
low expression of miR-21 in HCC patients. Reasons for this conflicting data may be due to differences in
detection techniques, as well as, differences in patient cohorts.
The content of serum exosomes has been associated with aggressiveness, prognosis and survival of HCC
patients. For instance, downregulation of miR-718 in serum exosomes was associated with the recurrence
of HCC after liver transplantation in 59 HCC patients. HOXB8 was identified as a potential target gene
of miR-718, such that the downregulation of miR-718 resulted in the overexpression of HOXB8 in HCC
patients. High expression of HOXB8 plays an important role in the progression and recurrence of HCC .
[20]
Exosomes extracted from serum samples collected from two cohorts of HCC patients showed high levels of
miR-125b which was an independent predictive factor for postoperative recurrence and overall survival of
HCC patients . Serum exosomal miR-665 levels were significantly higher in HCC patients than those in
[39]
healthy subjects. Additionally, exosomal miR-665 levels were elevated in larger tumours with local invasion