Page 132 - Read Online
P. 132
Fatourou et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.62 Page 5 of 11
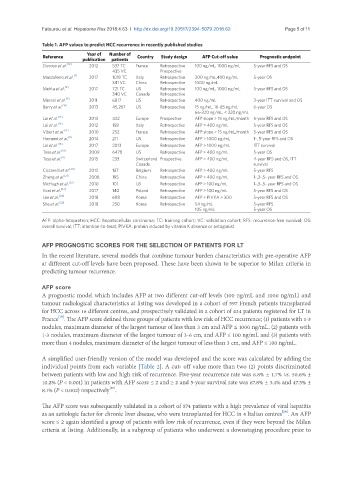
Table 1. AFP values to predict HCC recurrence in recently published studies
Year of Number of
Reference Country Study design AFP Cut-off value Prognostic endpoint
publication patients
Duvoux et al. [10] 2012 537 TC France Retrospective 100 ng/mL, 1000 ng/mL 5-year RFS and OS
435 VC Prospective
Mazzaferro et al. [7] 2017 1018 TC Italy Retrospective 200 ng/mL,400 ng/mL 5-year OS
341 VC China Retrospective 1000 ng/mL
Mehta et al. [8] 2017 721 TC US Retrospective 100 ng/mL, 1000 ng/mL 5-year RFS and OS
340 VC Canada Retrospective
Merani et al. [6] 2011 6817 US Retrospective 400 ng/mL 3-year ITT survival and OS
Berry et al. [15] 2013 45,267 US Retrospective 15 ng/mL, 16-65 ng/mL 6-year OS
66-320 ng/mL, < 320 ng/mL
Lai et al. [12] 2013 422 Europe Prospective AFP slope > 15 ng/mL/month 5-year RFS and OS
Lai et al. [16] 2012 158 Italy Retrospective AFP > 400 ng/mL 5-year RFS and OS
Vibert et al. [17] 2010 252 France Retrospective AFP slope > 15 ng/mL/month 5-year RFS and OS
[11]
Hameed et al. 2014 211 US Retrospective AFP > 1000 ng/mL 1-, 5-year RFS and OS
Lai et al. [18] 2017 2013 Europe Retrospective AFP > 1000 ng/mL ITT survival
Toso et al. [19] 2009 6478 US Retrospective AFP > 400 ng/mL 5-year OS
Toso et al. [9] 2015 233 Switzerland Prospective AFP > 400 ng/mL 4-year RFS and OS, ITT
Canada survival
Ciccarelli et al. [20] 2012 137 Belgium Retrospective AFP > 400 ng/mL 5-year RFS
Zheng et al. [21] 2008 195 China Retrospective AFP > 400 ng/mL 1-,3-,5- year RFS and OS
McHugh et al. [22] 2010 101 US Retrospective AFP > 100 ng/mL 1-,3-,5- year RFS and OS
Grat et al. [23] 2017 140 Poland Retrospective AFP > 100 ng/mL 5-year RFS and OS
Lee et al. [24] 2018 688 Korea Retrospective AFP + PIVKA > 300 5-year RFS and OS
She et al. [25] 2018 250 Korea Retrospective 54 ng/mL 5-year RFS
105 ng/mL 5-year OS
AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; TC: training cohort; VC: validation cohort; RFS: recurrence-free survival; OS:
overall survival; ITT: intention-to-treat; PIVKA: protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist
AFP PROGNOSTIC SCORES FOR THE SELECTION OF PATIENTS FOR LT
In the recent literature, several models that combine tumour burden characteristics with pre-operative AFP
at different cut-off levels have been proposed. These have been shown to be superior to Milan criteria in
predicting tumour recurrence.
AFP score
A prognostic model which includes AFP at two different cut-off levels (100 ng/mL and 1000 ng/mL) and
tumour radiological characteristics at listing was developed in a cohort of 597 French patients transplanted
for HCC across 16 different centres, and prospectively validated in a cohort of 434 patients registered for LT in
France . The AFP score defined three groups of patients with low risk of HCC recurrence; (1) patients with 1-3
[10]
nodules, maximum diameter of the largest tumour of less than 3 cm and AFP ≤ 1000 ng/mL, (2) patients with
1-3 nodules, maximum diameter of the largest tumour of 3-6 cm, and AFP ≤ 100 ng/mL and (3) patients with
more than 4 nodules, maximum diameter of the largest tumour of less than 3 cm, and AFP ≤ 100 ng/mL.
A simplified user-friendly version of the model was developed and the score was calculated by adding the
individual points from each variable [Table 2]. A cut- off value more than two (2) points discriminated
between patients with low and high risk of recurrence. Five-year recurrence rate was 8.8% ± 1.7% vs. 50.6% ±
10.2% (P < 0.001) in patients with AFP score ≤ 2 and ≥ 2 and 5-year survival rate was 67.8% ± 3.4% and 47.5% ±
[10]
8.1% (P < 0.002) respectively .
The AFP score was subsequently validated in a cohort of 574 patients with a high prevalence of viral hepatitis
[26]
as an aetiologic factor for chronic liver disease, who were transplanted for HCC in 4 Italian centres . An AFP
score ≤ 2 again identified a group of patients with low risk of recurrence, even if they were beyond the Milan
criteria at listing. Additionally, in a subgroup of patients who underwent a downstaging procedure prior to