Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Page 2 of 10 Yapali et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:24 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.57
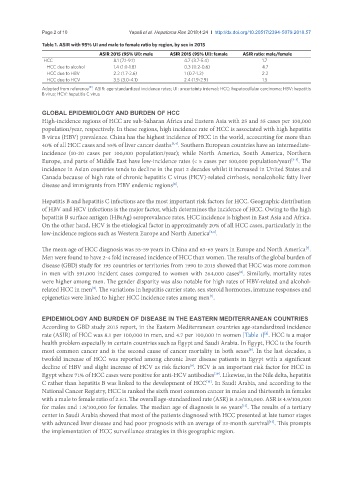
Table 1. ASIR with 95% UI and male to female ratio by region, by sex in 2015
ASIR 2015 (95% UI): male ASIR 2015 (95% UI): female ASIR ratio: male/female
HCC 8.1 (7.1-9.1) 4.7 (3.7-5.4) 1.7
HCC due to alcohol 1.4 (1.0-1.8) 0.3 (0.2-0.6) 4.7
HCC due to HBV 2.2 (1.7-2.6) 1 (0.7-1.2) 2.2
HCC due to HCV 3.5 (3.0-4.1) 2.4 (1.9-2.9) 1.5
Adapted from reference . ASIR: age-standardized incidence rates; UI: uncertainty interval; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV: hepatitis
[8]
B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus
GLOBAL EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BURDEN OF HCC
High-incidence regions of HCC are sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern Asia with 25 and 35 cases per 100,000
population/year, respectively. In these regions, high incidence rate of HCC is associated with high hepatitis
B virus (HBV) prevalence. China has the highest incidence of HCC in the world, accounting for more than
40% of all HCC cases and 55% of liver cancer deaths . Southern European countries have an intermediate-
[3,4]
incidence (10-20 cases per 100,000 population/year); while North America, South America, Northern
Europe, and parts of Middle East have low-incidence rates (< 5 cases per 100,000 population/year) . The
[3-5]
incidence in Asian countries tends to decline in the past 2 decades whilst it increased in United States and
Canada because of high rate of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related cirrhosis, nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease and immigrants from HBV endemic regions .
[4]
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections are the most important risk factors for HCC. Geographic distribution
of HBV and HCV infections is the major factor, which determines the incidence of HCC. Owing to the high
hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroprevalance rates, HCC incidence is highest in East Asia and Africa.
On the other hand, HCV is the etiological factor in approximately 20% of all HCC cases, particularly in the
low-incidence regions such as Western Europe and North America .
[3,6]
The mean age of HCC diagnosis was 55-59 years in China and 63-65 years in Europe and North America .
[7]
Men were found to have 2-4 fold increased incidence of HCC than women. The results of the global burden of
disease (GBD) study for 195 countries or territories from 1990 to 2015 showed that HCC was more common
in men with 591,000 incident cases compared to women with 264,000 cases . Similarly, mortality rates
[8]
were higher among men. The gender disparity was also notable for high rates of HBV-related and alcohol-
related HCC in men . The variations in hepatitis carrier state, sex steroid hormones, immune responses and
[8]
epigenetics were linked to higher HCC incidence rates among men .
[7]
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BURDEN OF DISEASE IN THE EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN COUNTRIES
According to GBD study 2015 report, in the Eastern Mediterranean countries age-standardized incidence
rate (ASIR) of HCC was 8.1 per 100,000 in men, and 4.7 per 100,000 in women [Table 1] . HCC is a major
[8]
health problem especially in certain countries such as Egypt and Saudi Arabia. In Egypt, HCC is the fourth
most common cancer and is the second cause of cancer mortality in both sexes . In the last decades, a
[8]
twofold increase of HCC was reported among chronic liver disease patients in Egypt with a significant
decline of HBV and slight increase of HCV as risk factors . HCV is an important risk factor for HCC in
[9]
Egypt where 71% of HCC cases were positive for anti-HCV antibodies . Likewise, in the Nile delta, hepatitis
[10]
C rather than hepatitis B was linked to the development of HCC . In Saudi Arabia, and according to the
[11]
National Cancer Registry, HCC is ranked the sixth most common cancer in males and thirteenth in females
with a male to female ratio of 2.6:1. The overall age-standardized rate (ASR) is 3.5/100,000. ASR is 4.9/100,000
for males and 1.8/100,000 for females. The median age of diagnosis is 66 years . The results of a tertiary
[12]
center in Saudi Arabia showed that most of the patients diagnosed with HCC presented at late tumor stages
with advanced liver disease and had poor prognosis with an average of 33-month survival . This prompts
[12]
the implementation of HCC surveillance strategies in this geographic region.