Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Feun et al. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
functional vector represents a novel immunotherapy
approach to treat HCC.
PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has been associated with T-cell
exhaustion in chronic hepatitis virus infection. [25]
Inhibition of T-cell activation is due to PD-1 ligation,
which causes recruitment of SHP-2 phosphatase. This
in turn inhibits PI3K activity and downstream activation
of AKt, with dampening of T-cell receptor signaling.
PD-1/PD-L-1 involvement in chronic viral infection-
associated T-cell exhaustion was first shown in a
murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis model. [26] PD-1/
PD-L-1 blockade can produce functional recovery of
T-cells, cytokine secretion, cytotoxic capability and
decreased viral load.
IMMUNOTHERAPY TRIALS IN HCC
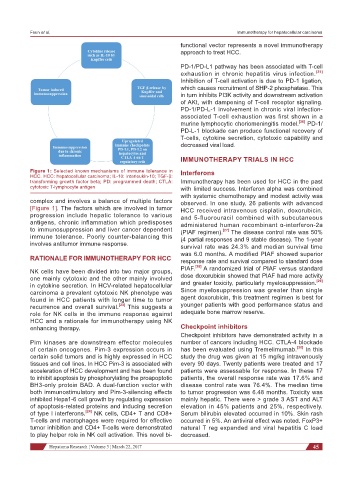
Figure 1: Selected known mechanisms of immune tolerance in Interferons
HCC. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; IL-10: interleukin-10; TGF-β:
transforming growth factor beta; PD: programmed death; CTLA: Immunotherapy has been used for HCC in the past
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen with limited success. Interferon alpha was combined
with systemic chemotherapy and modest activity was
complex and involves a balance of multiple factors observed. In one study, 26 patients with advanced
[Figure 1]. The factors which are involved in tumor HCC received intravenous cisplatin, doxorubicin,
progression include hepatic tolerance to various and 5-fluorouracil combined with subcutaneous
antigens, chronic inflammation which predisposes administered human recombinant α-interferon-2a
to immunosuppression and liver cancer dependent (PIAF regimen). [27] The disease control rate was 50%
immune tolerance. Poorly counter-balancing this (4 partial responses and 9 stable disease). The 1-year
involves antitumor immune response. survival rate was 24.3% and median survival time
was 6.0 months. A modified PIAF showed superior
RATIONALE FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR HCC response rate and survival compared to standard dose
NK cells have been divided into two major groups, PIAF. [28] A randomized trial of PIAF versus standard
one mainly cytotoxic and the other mainly involved dose doxorubicin showed that PIAF had more activity
[29]
in cytokine secretion. In HCV-related hepatocellular and greater toxicity, particularly myelosuppression.
carcinoma a prevalent cytotoxic NK phenotype was Since myelosuppression was greater than single
found in HCC patients with longer time to tumor agent doxorubicin, this treatment regimen is best for
recurrence and overall survival. [23] This suggests a younger patients with good performance status and
role for NK cells in the immune response against adequate bone marrow reserve.
HCC and a rationale for immunotherapy using NK
enhancing therapy. Checkpoint inhibitors
Checkpoint inhibitors have demonstrated activity in a
Pim kinases are downstream effector molecules number of cancers including HCC. CTLA-4 blockade
of certain oncogenes. Pim-3 expression occurs in has been evaluated using Tremelimumab. [30] In this
certain solid tumors and is highly expressed in HCC study the drug was given at 15 mg/kg intravenously
tissues and cell lines. In HCC Pim-3 is associated with every 90 days. Twenty patients were treated and 17
acceleration of HCC development and has been found patients were assessable for response. In these 17
to inhibit apoptosis by phosphorylating the proapoptotic patients, the overall response rate was 17.6% and
BH3-only protein BAD. A dual-function vector with disease control rate was 76.4%. The median time
both immunostimulatory and Pim-3-silencing effects to tumor progression was 6.48 months. Toxicity was
inhibited Hepa1-6 cell growth by regulating expression mainly hepatic. There were > grade 3 AST and ALT
of apoptosis-related proteins and inducing secretion elevation in 45% patients and 25%, respectively.
of type I interferons. [24] NK cells, CD4+ T and CD8+ Serum bilirubin elevated occurred in 10%. Skin rash
T-cells and macrophages were required for effective occurred in 5%. An antiviral effect was noted. FoxP3+
tumor inhibition and CD4+ T-cells were demonstrated natural T reg expanded and viral hepatitis C load
to play helper role in NK cell activation. This novel bi- decreased.
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ March 22, 2017 45