Page 172 - Read Online
P. 172
Page 14 Ribovski et al. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucleic Acids 2023;4:283-305 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/evcna.2023.26
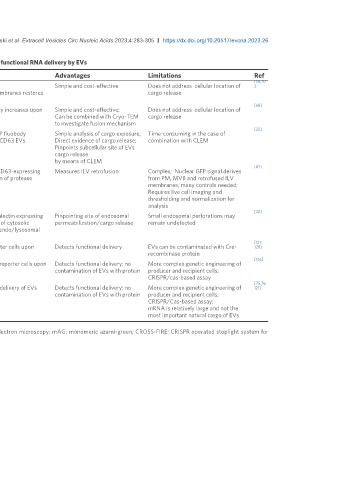
Table 2. Assays to detect membrane fusion, cargo exposure, subcellular site of cargo release, and functional RNA delivery by EVs
Assay type Mechanism Advantages Limitations Ref
[58,117
Fluorescence Membrane fusion Lipid-mixing/ Simple and cost-effective Does not address cellular location of ]
quenching based on Fusion of the PS:PC:Chol-R18 liposomes with lipid membranes restores cargo release
R18 fluorescence
[68]
DiI-DiD-based FRET Membrane fusion (EVs with Lipid-mixing/DiI and DiD as FRET pair (donor intensity increases upon Simple and cost-effective; Does not address cellular location of
assay LUVs) fusion) Can be combined with Cryo-TEM cargo release
to investigate fusion mechanism
[22]
Nanobody assay; EV cargo exposure; detection Punctate structure formation upon binding of anti-GFP fluobody Simple analysis of cargo exposure; Time-consuming in the case of
CLEM of subcellular site of cargo (expressed in recipient cells) to GFP cargo from GFP-CD63 EVs Direct evidence of cargo release; combination with CLEM
release Pinpoints subcellular site of EVs
cargo release
by means of CLEM
[87]
Retrofusion assay Membrane fusion (ILV Nuclear accumulation of NLS-GFP in NLS-GFP-TCS-CD63-expressing Measures ILV retrofusion Complex; Nuclear GFP signal derives
retrofusion) cells that co-express split TEV protease, upon addition of protease from PM, MVB and retrofused ILV
dimerizer membranes; many controls needed;
Requires live cell imaging and
thresholding and normalization for
analysis
[22]
Galectin assay Endosomal permeabilization Endosomal accumulation of mAG-galectin in mAG-galectin expressing Pinpointing site of endosomal Small endosomal perforations may
cells upon endosomal permeabilization, i.e., exposure of cytosolic permeabilization/cargo release remain undetected
galectins to β-galactosides present exclusively in the endo/lysosomal
lumen.
[127,
Cre-recombinase mRNA delivery RFP to GFP fluorescence conversion in recipient reporter cells upon Detects functional delivery EVs can be contaminated with Cre- 128]
addition of Cre-recombinase mRNA-containing EVs recombinase protein
[126]
CROSS-FIRE sgRNA delivery mCherry to GFP fluorescence conversion in recipient reporter cells upon Detects functional delivery; no More complex genetic engineering of
addition of sgRNA-containing EVs contamination of EVs with protein producer and recipient cells;
CRISPR/cas-based assay
[75,76,
REMD mRNA delivery Luciferase expression in recipient reporter cells upon delivery of EVs Detects functional delivery; no More complex genetic engineering of 121]
containing NanoLuc mRNA with a stop codon contamination of EVs with protein producer and recipient cells;
CRISPR/Cas-based assay;
mRNA is relatively large and not the
most important natural cargo of EVs
LUVs: large unilamellar vesicles; TEM: transmission electron microscopy; CLEM: correlative light and electron microscopy; mAG: monomeric azami-green; CROSS-FIRE: CRISPR operated stoplight system for
functional intercellular RNA exchange; REMD: RNA-editing-based mRNA delivery.
different proteins play a role.