Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Biersack. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:1-17 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.09 Page 5
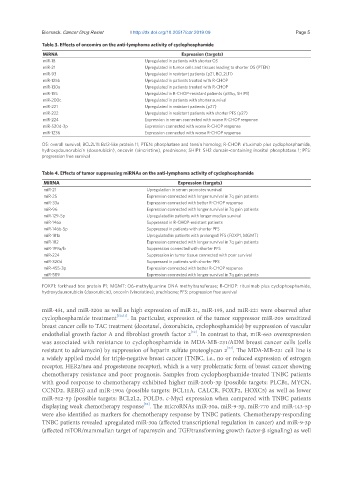
Table 3. Effects of oncomirs on the anti-lymphoma activity of cyclophosphamide
MiRNA Expression (targets)
miR-18 Upregulated in patients with shorter OS
miR-21 Upregulated in tumor cells and tissues leading to shorter OS (PTEN)
miR-93 Upregulated in resistant patients (p21, BCL2L11)
miR-125b Upregulated in patients treated with R-CHOP
miR-130a Upregulated in patients treated with R-CHOP
miR-155 Upregulated in R-CHOP-resistant patients (p85α, SHIP1)
miR-200c Upregulated in patients with shorter survival
miR-221 Upregulated in resistant patients (p27)
miR-222 Upregulated in resistant patients with shorter PFS (p27)
miR-224 Expression in serum connected with worse R-CHOP response
miR-520d-3p Expression connected with worse R-CHOP response
miR-1236 Expression connected with worse R-CHOP response
OS: overall survival; BCL2L11: Bcl2-like protein 11; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; R-CHOP: rituximab plus cyclophosphamide,
hydroxydaunorubicin (doxorubicin), oncovin (vincristine), prednisone; SHIP1: SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase 1; PFS:
progression free survival
Table 4. Effects of tumor suppressing miRNAs on the anti-lymphoma activity of cyclophosphamide
MiRNA Expression (targets)
miR-21 Upregulation in serum promotes survival
miR-25 Expression connected with longer survival in 7q gain patients
miR-33a Expression connected with better R-CHOP response
miR-96 Expression connected with longer survival in 7q gain patients
miR-129-5p Upregulated in patients with longer median survival
miR-146a Suppressed in R-CHOP-resistant patients
miR-146b-5p Suppressed in patients with shorter PFS
miR-181a Upregulated in patients with prolonged PFS (FOXP1, MGMT)
miR-182 Expression connected with longer survival in 7q gain patients
miR-199a/b Suppression connected with shorter PFS
miR-224 Suppression in tumor tissue connected with poor survival
miR-320d Suppressed in patients with shorter PFS
miR-455-3p Expression connected with better R-CHOP response
miR-589 Expression connected with longer survival in 7q gain patients
FOXP1: forkhead box protein P1; MGMT: O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase; R-CHOP: rituximab plus cyclophosphamide,
hydroxydaunorubicin (doxorubicin), oncovin (vincristine), prednisone; PFS: progression free survival
miR-451, and miR-3200 as well as high expression of miR-21, miR-195, and miR-221 were observed after
cyclophosphamide treatment [50,51] . In particular, expression of the tumor suppressor miR-205 sensitized
breast cancer cells to TAC treatment (docetaxel, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide) by suppression of vascular
[52]
endothelial growth factor A and fibroblast growth factor 2 . In contrast to that, miR-663 overexpression
was associated with resistance to cyclophosphamide in MDA-MB-231/ADM breast cancer cells (cells
[53]
resistant to adriamycin) by suppression of heparin sulfate proteoglycan 2 . The MDA-MB-231 cell line is
a widely applied model for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC, i.e., no or reduced expression of estrogen
receptor, HER2/neu and progesterone receptor), which is a very problematic form of breast cancer showing
chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis. Samples from cyclophosphamide-treated TNBC patients
with good response to chemotherapy exhibited higher miR-200b-3p (possible targets: PLCB1, MYCN,
CCND2, RERG) and miR-190a (possible targets: BCL11A, CALCR, FOXP2, HOXC5) as well as lower
miR-512-5p (possible targets: BCL2L2, POLD3, c-Myc) expression when compared with TNBC patients
[54]
displaying weak chemotherapy response . The microRNAs miR-30a, miR-9-3p, miR-770 and miR-143-5p
were also identified as markers for chemotherapy response by TNBC patients. Chemotherapy-responding
TNBC patients revealed upregulated miR-30a (affected transcriptional regulation in cancer) and miR-9-3p
(affected mTOR/mammalian target of rapamycin and TGF/transforming growth factor-β signaling) as well