Page 133 - Read Online
P. 133
Page 330 White et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:326-34 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.16
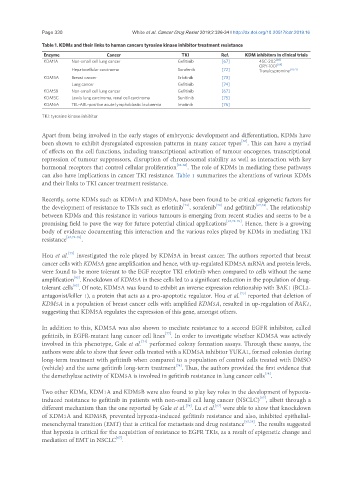
Table 1. KDMs and their links to human cancers tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment resistance
Enzyme Cancer TKI Ref. KDM inhibitors in clinical trials
KDM1A Non-small cell lung cancer Gefitinib [67] 4SC-202 [68]
ORY-1001 [69]
Hepatocellular carcinoma Sorafenib [72] Tranylcypromine [70,71]
KDM5A Breast cancer Erlotinib [73]
Lung cancer Gefitinib [74]
KDM5B Non-small cell lung cancer Gefitinib [67]
KDM5C Lewis lung carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma Sunitinib [75]
KDM6A TEL-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Imatinib [76]
TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Apart from being involved in the early stages of embryonic development and differentiation, KDMs have
[60]
been shown to exhibit dysregulated expression patterns in many cancer types . This can have a myriad
of effects on the cell functions, including transcriptional activation of tumour oncogenes, transcriptional
repression of tumour suppressors, disruption of chromosomal stability as well as interaction with key
hormonal receptors that control cellular proliferation [64-66] . The role of KDMs in mediating these pathways
can also have implications in cancer TKI resistance. Table 1 summarizes the alterations of various KDMs
and their links to TKI cancer treatment resistance.
Recently, some KDMs such as KDM1A and KDM5A, have been found to be critical epigenetic factors for
[73]
the development of resistance to TKIs such as erlotinib , sorafenib and gefitinib [67,74] . The relationship
[72]
between KDMs and this resistance in various tumours is emerging from recent studies and seems to be a
promising field to pave the way for future potential clinical applications [67,72-76] . Hence, there is a growing
body of evidence documenting this interaction and the various roles played by KDMs in mediating TKI
resistance [67,72-76] .
[73]
Hou et al. investigated the role played by KDM5A in breast cancer. The authors reported that breast
cancer cells with KDM5A gene amplification and hence, with up-regulated KDM5A mRNA and protein levels,
were found to be more tolerant to the EGF receptor TKI erlotinib when compared to cells without the same
[62]
amplification . Knockdown of KDM5A in these cells led to a significant reduction in the population of drug-
tolerant cells . Of note, KDM5A was found to exhibit an inverse expression relationship with BAK1 (BCL2-
[62]
[73]
antagonist/killer 1), a protein that acts as a pro-apoptotic regulator. Hou et al. reported that deletion of
KDM5A in a population of breast cancer cells with amplified KDM5A, resulted in up-regulation of BAK1,
suggesting that KDM5A regulates the expression of this gene, amongst others.
In addition to this, KDM5A was also shown to mediate resistance to a second EGFR inhibitor, called
gefitinib, in EGFR-mutant lung cancer cell lines . In order to investigate whether KDM5A was actively
[77]
[74]
involved in this phenotype, Gale et al. performed colony formation assays. Through these assays, the
authors were able to show that fewer cells treated with a KDM5A inhibitor YUKA1, formed colonies during
long-term treatment with gefitinib when compared to a population of control cells treated with DMSO
[74]
(vehicle) and the same gefitinib long-term treatment . Thus, the authors provided the first evidence that
[74]
the demethylase activity of KDM5A is involved in gefitinib resistance in lung cancer cells .
Two other KDMs, KDM1A and KDM5B were also found to play key roles in the development of hypoxia-
induced resistance to gefitinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) , albeit through a
[67]
[67]
[74]
different mechanism than the one reported by Gale et al. . Lu et al. were able to show that knockdown
of KDM1A and KDM5B, prevented hypoxia-induced gefitinib resistance and also, inhibited epithelial-
mesenchymal transition (EMT) that is critical for metastasis and drug resistance [67,78] . The results suggested
that hypoxia is critical for the acquisition of resistance to EGFR TKIs, as a result of epigenetic change and
[67]
mediation of EMT in NSCLC .