Page 72 - Read Online
P. 72
Zhang et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2024;7:30 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2024.62 Page 9 of 13
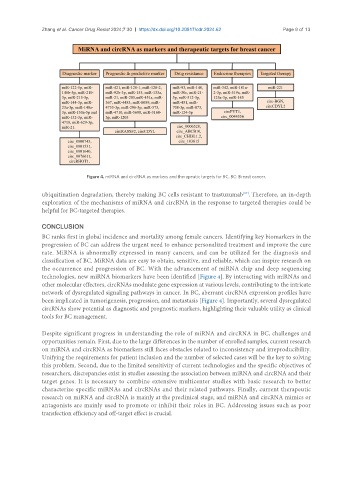
Figure 4. miRNA and circRNA as markers and therapeutic targets for BC. BC: Breast cancer.
[87]
ubiquitination degradation, thereby making BC cells resistant to trastuzumab . Therefore, an in-depth
exploration of the mechanisms of miRNA and circRNA in the response to targeted therapies could be
helpful for BC-targeted therapies.
CONCLUSION
BC ranks first in global incidence and mortality among female cancers. Identifying key biomarkers in the
progression of BC can address the urgent need to enhance personalized treatment and improve the cure
rate. MiRNA is abnormally expressed in many cancers, and can be utilized for the diagnosis and
classification of BC. MiRNA data are easy to obtain, sensitive, and reliable, which can inspire research on
the occurrence and progression of BC. With the advancement of miRNA chip and deep sequencing
technologies, new miRNA biomarkers have been identified [Figure 4]. By interacting with miRNAs and
other molecular effectors, circRNAs modulate gene expression at various levels, contributing to the intricate
network of dysregulated signaling pathways in cancer. In BC, aberrant circRNA expression profiles have
been implicated in tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis [Figure 4]. Importantly, several dysregulated
circRNAs show potential as diagnostic and prognostic markers, highlighting their valuable utility as clinical
tools for BC management.
Despite significant progress in understanding the role of miRNA and circRNA in BC, challenges and
opportunities remain. First, due to the large differences in the number of enrolled samples, current research
on miRNA and circRNA as biomarkers still faces obstacles related to inconsistency and irreproducibility.
Unifying the requirements for patient inclusion and the number of selected cases will be the key to solving
this problem. Second, due to the limited sensitivity of current technologies and the specific objectives of
researchers, discrepancies exist in studies assessing the association between miRNA and circRNA and their
target genes. It is necessary to combine extensive multicenter studies with basic research to better
characterize specific miRNAs and circRNAs and their related pathways. Finally, current therapeutic
research on miRNA and circRNA is mainly at the preclinical stage, and miRNA and circRNA mimics or
antagonists are mainly used to promote or inhibit their roles in BC. Addressing issues such as poor
transfection efficiency and off-target effect is crucial.