Page 38 - Read Online
P. 38
Page 305 Brenac et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:296-315 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.49
[31]
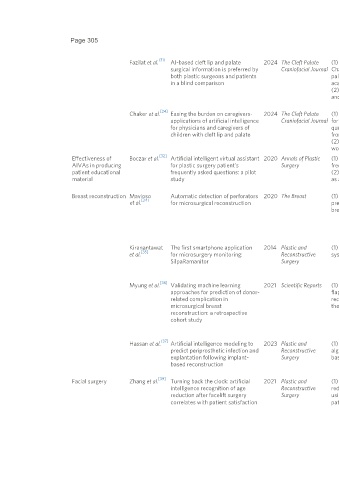
Fazilat et al. AI-based cleft lip and palate 2024 The Cleft Palate (1) Compare the quality and readability of (1) Plastic surgeons rated ChatGPT-generated
surgical information is preferred by Craniofacial Journal ChatGPT-generated response to cleft lip and information higher for comprehensiveness (P < 0.0001)
both plastic surgeons and patients palate questions against those provided by and clarity (P < 0.001), and both plastic surgeons and
in a blind comparison academic and professional sources non-medical individuals preferred ChatGPT 60.88% and
(2) Evaluate comprehensiveness, clarity, accuracy, 60.46% of the time, respectively
and preference (2) ChatGPT and the academic and professional sources
exceeded the NIH’s recommended readability level
[24]
Chaker et al. Easing the burden on caregivers- 2024 The Cleft Palate (1) Assess the accuracy of AI-generated responses (1) AI-generated information had a 69% accuracy rate
applications of artificial intelligence Craniofacial Journal for cleft lip and palate repair postoperative compared to expert responses, showing potential in
for physicians and caregivers of questions by comparing them to expert responses creating patient education materials
children with cleft lip and palate from pediatric plastic surgeons (2) Although AI can reduce physician workload, more
(2) Evaluate ChatGPT’s ability to reduce physician personalized outputs are necessary for higher-quality
workload by generating patient education material patient care
[32]
Effectiveness of Boczar et al. Artificial intelligent virtual assistant 2020 Annals of Plastic (1) Evaluate the accuracy of AIVAs in answering (1) AIVAs answered 92.3% of plastic surgery FAQs
AIVAs in producing for plastic surgery patient’s Surgery frequently asked plastic surgery questions correctly, although participants marked only 83.3% of
patient educational frequently asked questions: a pilot (2) Assess patient perceptions of AIVA responses responses as accurate
material study as a source of patient-facing information (2) According to a Likert scale, patients were neutral
regarding AIVAs’ potential to replace human assistance
Breast reconstruction Mavioso Automatic detection of perforators 2020 The Breast (1) Reduce duration and subjectivity of the (1) Reduced time for Angio CT from 2 h per patient to 30
et al. [34] for microsurgical reconstruction preoperative Angio CT using CV for DIEP flaps min
breast reconstruction (2) Automatic perforator detection was better with the
software compared to the radiology team when
estimating large vessels
(3) Software showed more difficulties estimating the
caliber of smaller perforators
Kiranantawat The first smartphone application 2014 Plastic and (1) Develop and evaluate a free flap monitoring (1) The smartphone application is sensitive (94%),
[35]
et al. for microsurgery monitoring: Reconstructive system using mobile phone technology specific (98%), and accurate for venous (93%) and
SilpaRamanitor Surgery arterial occlusion (95%)
(2) Potential applications for early detection of flap
failure
[36]
Myung et al. Validating machine learning 2021 Scientific Reports (1) Evaluate a ML prediction model for abdominal (1) Neuralnet was identified as the most effective ML
approaches for prediction of donor- flap donor site complications in breast package for predicting donor site complications
related complication in reconstruction and determine factors influencing (2) Significant factors affecting complications included
microsurgical breast these complications using logistic regression the size of the fascial defect, history of diabetes, muscle-
reconstruction: a retrospective sparing type, and adjuvant chemotherapy
2
cohort study (3) The risk cutoff for fascial defect was 37.5 cm , with a
high-risk group showing a 26% complication rate
compared to 1.7% in the low-risk group
[37]
Hassan et al. Artificial intelligence modeling to 2023 Plastic and (1) Develop, validate and evaluate the use of ML (1) ML showed strong discriminatory performance in
predict periprosthetic infection and Reconstructive algorithms to predict complications of implant- predicting periprosthetic infection and explantation, with
explantation following implant- Surgery based reconstructions AUC values of 0.73 and 0.78, respectively
based reconstruction (2) ML identified 9 and 12 predictors of periprosthetic
infection and explantation, respectively
[39]
Facial surgery Zhang et al. Turning back the clock: artificial 2021 Plastic and (1) Evaluate the effectiveness of facelift surgery in (1) Four neural networks accurately estimated
intelligence recognition of age Reconstructive reducing perceived age and patient satisfaction preoperative age, with an average accuracy score of
reduction after facelift surgery Surgery using convolutional neural networks and FACE-Q 100.8
correlates with patient satisfaction patient-reported outcomes